More Stainless Steel Tank Manufacturers
Thanks to these qualities, stainless steel tanks can store a wide variety of substances, including food, beverages, water, gas, chemicals, and even hazardous materials.
Many industries and sectors rely on these storage tanks. Examples include the industrial, construction, and educational sectors. Stainless steel tanks offer essential storage solutions for factories, schools, and residential buildings.
History of Stainless Steel Tanks
The emergence of steel storage tanks is deeply connected to the growth of industrial society in Western countries during the mid-nineteenth century. Notably, the expansion of the oil and energy industry drove advancements in storage technology. Prior to the Industrial Revolution, items like oil were typically kept in wooden barrels. However, the swift pace of industrial progress soon rendered this method impractical.
The birth of oil drilling in the U.S. in 1859 introduced a new potential source for commercial lighting. While electricity soon took over this role, oil and petroleum became crucial in the emerging automobile industry. As automobile innovation surged in the late 1800s, finding sizable and safe storage methods for substances like hydrocarbons became essential. Riveted steel tanks swiftly replaced wooden containers due to their superior safety, durability, and greater storage capacities. Interestingly, the evolution of steel tanks in the United States mirrors the eventual rise of similar storage systems globally.
Throughout the twentieth century, the usage of steel tanks continued to evolve due to various significant events. During World War II, there was a temporary shift to using black carbon steel instead of galvanized steel for tank production. The rise of gas service stations in the U.S., driven by the booming automobile industry, led to the increased popularity of underground tank storage. In the 1960s, storage tanks saw substantial improvements in corrosion resistance thanks to new production materials and innovative designs or accessories, such as fiberglass reinforcement and coal tar epoxy coatings. As the century drew to a close, there was a resurgence of above-ground tank storage, primarily because of environmental concerns related to underground tanks. In the 21st century, steel storage tanks and their counterparts have become more durable and essential than ever in our modern industrial society.
Stainless Steel Tank Materials
Steel stands out as the most prevalent material for manufacturing storage tanks. Among the various options, stainless steel is particularly favored due to its ease of manipulation and ability to maintain cleanliness and sterility. Stainless steels can be categorized into several types. Austenitic stainless steel, rich in nickel, manganese, and nitrogen, is the most popular due to its excellent welding properties. Ferritic stainless steel, which contains high levels of chromium, features a cubic crystalline structure. Duplex stainless steels, or ferritic-austenitic stainless steels, are engineered to combine the best attributes of both categories.
While stainless steel construction is often the go-to choice for storage tanks, it is important to remember that it is not the only option. Storage tanks can also be made from concrete and various types of plastic, such as thermoplastic or polyethylene. Plastic storage tanks, in particular, are becoming more common. These plastic tanks often offer better chemical resistance or cost savings compared to their steel counterparts.
Stainless Steel Tank Production
Stainless steel tanks are created through a meticulous multi-step process involving several stages of fabrication and assembly. We begin with the design phase, where the engineers craft detailed specifications and blueprints tailored to the tank’s specific requirements and intended use. Once the design is finalized, they move on to the manufacturing phase. They select sheets or plates of stainless steel, chosen for their thickness and corrosion resistance properties. These sheets, typically composed of alloys containing iron, carbon, and other elements, are then cut and shaped. Using techniques like laser cutting or shearing, they form the individual components of the tank, including the cylindrical body, top and bottom heads, and any additional fittings or attachments.
The formed components are then subjected to processes like welding or rolling to join them together and create watertight, structurally sound tanks. Welding, a commonly used method, involves heating the edges of the components and fusing them using electrical currents or gas flames, ensuring strong, durable joints. For larger tanks, rolling is employed, where the components are rolled and welded to form the cylindrical body.
Once they assemble the tank structure, they proceed with several finishing processes to enhance its appearance and resistance to corrosion. These include grinding, polishing, and passivation. Grinding and polishing smooth out any rough surfaces or weld seams, while passivation removes impurities and forms a protective oxide layer on the stainless steel surface, reducing the risk of corrosion.
The tanks are inspected for quality assurance. This involves checking for any defects, such as leaks or structural weaknesses, and conducting tests to ensure the tank meets the required industry standards and specifications. If any issues are identified, they are addressed and rectified before the tanks are ready for delivery or installation.
Overall, the production of stainless steel tanks involves a blend of design, material selection, fabrication, finishing, and quality control processes to create durable, corrosion-resistant, and reliable containers. These tanks are essential for various applications, including the storage of liquids, chemicals, or gasses.
Stainless Steel Tank Features and Customizations
Stainless steel tanks come with various features and customizations tailored to specific applications. One essential feature is the manway, an access opening in the tank used for maintenance, cleaning, or inspection. Manways can be positioned on the top or side of the tank and are available in different sizes and configurations, including hinged or bolted options. They offer convenience and easy access, ensuring efficient operations and reducing downtime.
Stainless steel tanks come in both vertical and horizontal designs. Vertical tanks save space and work well in height-restricted areas, while horizontal tanks fit installations with limited floor space or specific processes that need a horizontal setup. Choosing the right orientation depends on the available space and the application’s needs.
The variety in tank heights, diameters, and shapes allows us to customize them based on specific needs. We can design tanks with capacities ranging from small volumes to large storage options, accommodating different quantities of liquids or materials. The diameter affects stability and footprint, while the height dictates the vertical space needed. Additionally, we can tailor shapes to fit unique spaces or meet specific process requirements.
Secondary containment features are essential for safeguarding against leaks and spills, ensuring environmental protection. These include double walls, leak detection systems, and containment basins. Double-wall tanks consist of an inner tank encased within an outer tank, offering an added barrier against leaks. Leak detection systems, which may include sensors or alarms, swiftly identify any breaches or failures in the tank. Containment basins capture spills or leaks, preventing them from spreading and minimizing environmental impact. Together, these features enhance safety and bolster environmental protection.
To identify the essential features and customizations for a specific application, we need to consider various factors. These include the type of material being stored, the required storage capacity, the space available, any regulatory standards, and operational needs. Consulting with industry experts or engineers who specialize in tank design can be invaluable. They can assess the specific requirements, evaluate potential risks, and offer advice on the most suitable features, customizations, and secondary containment options to ensure optimal performance, safety, and compliance.
Stainless Steel Tank Accessories
Stainless steel tanks can be fitted with a range of accessories to boost their functionality and ease of use. A key accessory is the mounting system designed to secure the tanks to trucks or other transport vehicles. These systems offer stability and security during transit, keeping the tanks firmly in place and minimizing safety hazards. The choice of mounting accessories varies based on the vehicle type and the tank’s intended use.
Dip charts or level gauges are frequently used accessories for stainless steel tanks. These devices offer a visual readout of the liquid level within the tank, making it easy for operators to check contents without needing direct access. They are especially valuable for tanks storing liquids or chemicals, where precise level monitoring is essential for inventory control, process management, or safety. Usually, they feature calibrated markings or scales on the tank’s exterior, allowing operators to quickly assess the liquid level.
The necessity for these accessories varies based on the application and operational demands. For example, if we need to transport the tank on a truck or another mobile platform, a reliable mounting system is crucial to prevent any movement or damage during transit. Likewise, the requirement for dip charts or level gauges hinges on how critical accurate liquid level monitoring is and how accessible the tank is. When frequent level checks or remote monitoring are needed, dip charts or other level measurement devices become essential.
To figure out if these accessories are necessary, we need to think about several factors: the tank’s intended use, transportation needs, liquid level monitoring, and any relevant industry regulations or standards. It’s wise to consult with experts or tank suppliers experienced in the specific application. They can help us evaluate the requirements and choose the right accessories. Their guidance on mounting systems for transportation and level monitoring options will ensure we meet operational needs while staying compliant with safety and regulatory standards.
Types of Stainless Steel Tanks
Though all stainless steel tanks are designed to hold substances or materials, their specific purposes and appearances can vary greatly. Among the different types are storage tanks, pressure vessels, and atmospheric tanks, each tailored for distinct functions.
Storage tanks find applications across various industries, with notable use in brewing and agriculture. In these fields, stainless steel storage tanks take the form of vats, bins, and silos.
- Vats find their place in breweries, wineries, and distilleries, playing a crucial role in the refinement of beers, wines, and liquors.
- Silos, in contrast, are primarily found on farms, storing animal feed, grains, and other materials such as milk and solids. Unlike vats, silos are usually vertical structures.
- Stainless steel storage tanks are also utilized in wastewater and sewage management, food and beverage industries, and pharmaceuticals due to their corrosion resistance and hygiene. They maintain their effectiveness as long as they are cleaned regularly.
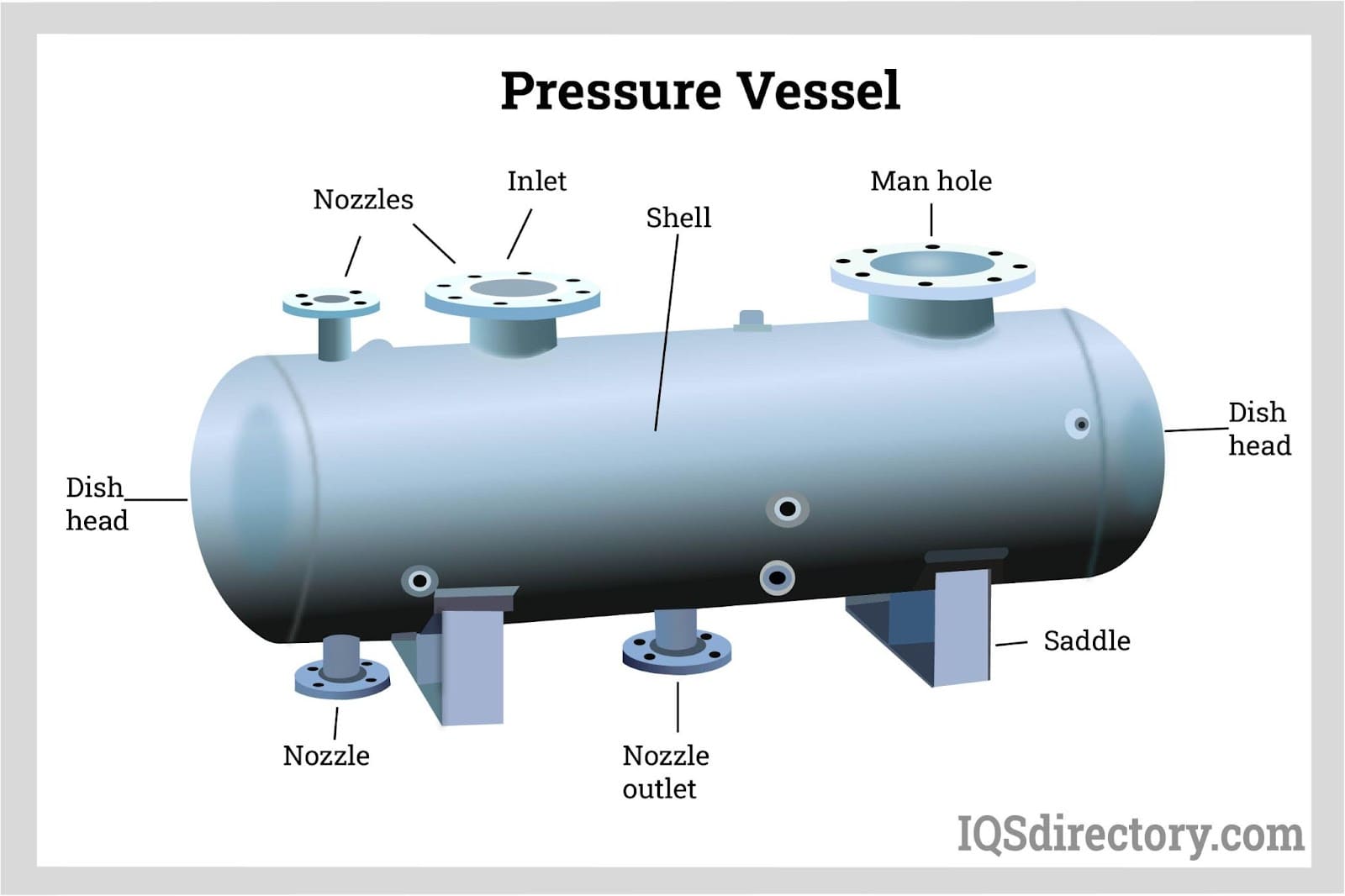
Pressure tanks rely on the thermal conductivity of stainless steel for insulation. They have various uses, with one of the most common being the storage of heat or cold for both short and long durations. Additionally, they are designed to contain gasses and liquids under different pressures, which may be significantly higher or lower than the surrounding ambient pressure.
- Pressure vessels come in various forms, such as domestic hot water storage tanks, pressurized hydraulic and pneumatic reservoirs, compressed air receivers, nuclear reactor vessels, pressure reactors, diving cylinders, distillation towers, and recompression chambers, among others.
- Atmospheric tanks are designed to hold liquids at atmospheric pressure rather than under pressure.
In the auto industry, specialized stainless steel tanks, known as gas tanks, are used to store fuel. To protect them from cracking, flaking, gasoline diffusion, and corrosion, these tanks are designed to be airtight and are coated with zinc or aluminum.
Similarly, stainless steel water tanks are crafted to store substantial volumes of water. They can be set up either above or below ground, serving diverse functions like irrigation, farming, food preparation, drinking, and fire-fighting. It’s important to regularly monitor these tanks due to the sensitive nature of water quality.
Food-grade tanks are designed for specific functions. They can either store perishable substances at controlled temperatures or mix and blend various ingredients. To ensure they maintain a sterile environment, tanks used for storage must be cleaned regularly. For mixing and blending, these tanks are equipped with motor-powered propellers to facilitate the process.
- In this context, milk tanks are stainless steel containers utilized on dairy farms to preserve milk freshness. Known also as bulk milk cooling tanks, they maintain raw milk at a chilled temperature until a milk hauler arrives to collect it.
Septic tanks are purpose-built storage containers that work as part of a larger sewage treatment or septic system. They come in different materials, including steel, concrete, plastic, or fiberglass. These tanks handle wastewater and process organic matter from homes using gravity, which means they don’t rely on mechanical power. Some models can hold up to a thousand gallons of water.
Fuel tanks play a crucial role in storing liquid fuels in settings like refineries. Essentially, they are any containers designed specifically to hold flammable liquids. Generally speaking, they can be divided into two categories:
Fixed roof tanks are designed for liquids with very high flash points—the temperatures at which a substance can ignite in the air. These tanks usually feature a conical lid welded to the tank’s structure.
- Floating roof tanks, on the other hand, have lids that float on the liquid’s surface. This category is divided into external floating roof tanks, which are suited for liquids with medium flash points, and internal floating roof tanks, which are used for liquids with low flash points. Some floating roof tanks combine a conical lid with a floating lid.
While setting up a water storage tank may seem straightforward, it’s crucial to consider design customizations carefully. Managing water scarcity is a key aspect of many applications, so special attention must be given to customizing nozzles and flanges to align with sensors and flow valves.
Additional types of fuel tanks are sphere tanks, bullet tanks, underground storage (UST) tanks, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) tanks.
Care for Stainless Steel Tanks
They must handle stainless steel tanks with great care, especially during their construction, installation, and transportation. To guard against potential leakage that could introduce toxins and compromise the tank’s contents, they often equip tanks with emergency bilge pumps or submersible pumps. Bilge pumps address leaks by removing liquids that escape into the tank, while submersible pumps manage leakage from within the tank itself. These pumps are typically used with tanks involved in groundwater treatment or pollutant extraction. However, despite these protective features, the only way to ensure that their tanks operate safely and efficiently is through regular inspections and thorough cleaning after each use.
Limitations and Overcoming Them
Stainless steel tanks bring many benefits but come with some limitations. They can be vulnerable to corrosion under certain conditions, despite their general resistance. Factors such as exposure to specific chemicals, high temperatures, or low-oxygen environments can still impact their durability. To address these challenges, manufacturers are developing advanced corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings, refining tank designs to reduce crevices and stagnant areas where corrosion might develop, and suggesting suitable materials based on the specific application and environment.
Another challenge involves the risk of stress corrosion cracking in stainless steel tanks subjected to both tensile stress and a corrosive environment. To address this, manufacturers utilize stress-relieving techniques during production and conduct rigorous testing and inspections to maintain the tanks’ structural integrity.
Furthermore, stainless steel tanks can come with constraints regarding their size and shape. Large tanks might pose difficulties with transportation, installation, and fabrication, necessitating specialized equipment and expert skills. To overcome these hurdles, manufacturers use advanced fabrication techniques, modular construction approaches, and collaborate closely with customers to create tanks that fulfill specific needs while navigating practical limitations.
Additionally, the initial expense of stainless steel tanks can be higher than that of other materials. Yet, their extended durability, resilience, and corrosion resistance can ultimately lead to a lower total cost of ownership over time, balancing out the upfront investment.
To address these challenges, manufacturers of stainless steel tanks are committed to ongoing research and development. They focus on enhancing materials, refining welding techniques, improving corrosion-resistant coatings, and advancing fabrication methods. By partnering with industry experts, leveraging computer-aided design and simulation tools, and keeping pace with industry standards and innovations, they aim to deliver cutting-edge solutions. This dedication helps overcome the limitations of stainless steel tanks, ensuring they offer dependable performance, long-lasting durability, and high customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless steel tanks are a popular choice across various industries due to their numerous advantages. Their standout feature is their remarkable corrosion resistance. Stainless steel resists rust, oxidation, and chemical reactions exceptionally well, making it perfect for storing corrosive substances like acids, alkalis, and certain chemicals. This resistance helps maintain the integrity and purity of the stored materials, minimizing the risk of contamination.
Additionally, these tanks are known for their durability and strength. They are built to endure harsh environmental conditions, high pressures, and mechanical stress. Their structural integrity ensures safe storage of liquids, gasses, and solids. The robust nature of stainless steel also allows the tanks to handle impacts, vibrations, and thermal stresses, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Stainless steel tanks provide exceptional hygiene and are easy to maintain. Their smooth, non-porous surfaces prevent the buildup of contaminants, bacteria, or residues, making them ideal for use in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Their resistance to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and fire further enhances their versatility across various environments.
In addition to their practical benefits, stainless steel tanks are environmentally friendly. They are fully recyclable, allowing for repurposing or recycling at the end of their lifecycle, which helps reduce waste and the demand for new raw materials. Their non-toxic nature ensures the safety of the stored substances and minimizes environmental impact.
Stainless steel tanks not only enhance the visual appeal of any setting but also project a professional image. They can be tailored with different finishes—polished, brushed, or painted—to achieve a look that fits seamlessly into both industrial and commercial environments.
In summary, stainless steel tanks offer numerous benefits: they resist corrosion, are durable and strong, maintain high hygiene standards, are environmentally friendly, and have a stylish appearance. These qualities make them a top choice for diverse applications, from chemical storage and food processing to pharmaceutical manufacturing and water treatment.
Stainless Steel Tank Applications
Stainless steel tanks serve a multitude of functions across different sectors. In the food and beverage industry, they are indispensable for storing and processing a variety of ingredients, drinks, dairy products, oils, and sauces. Their hygienic qualities help preserve the integrity and quality of these products. In the water industry, these tanks are utilized for holding potable water, wastewater, and other liquids, ensuring both cleanliness and protection against contamination.
In addition, stainless steel tanks are essential for the storage and transportation of gasses like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Their corrosion resistance and strength make them ideal for high-pressure gas applications. In the chemical sector, these tanks are employed for handling chemicals, acids, solvents, and other corrosive substances, offering durability and safeguarding against leaks or spills.
They are also used for managing hazardous materials, providing a safe solution for the storage and transport of hazardous waste, radioactive materials, and flammable substances. Their durability and resistance to corrosion make them a dependable choice for maintaining safety and meeting environmental regulations.
Stainless steel tanks find extensive use in the pharmaceutical and water treatment sectors because of their hygienic qualities, resistance to corrosion, and compatibility with various substances. In the pharmaceutical industry, these tanks serve to store, mix, and process ingredients, safeguarding product integrity and avoiding contamination. In water treatment, stainless steel tanks are key for purification, storage, and distribution, offering a robust and clean solution. They can be tailored with features such as manways, agitators, and level gauges to fit specific needs, and their durability against corrosive environments and ease of cleaning make them a top choice for these essential industries.
They extend their usefulness beyond industrial applications to educational environments, where they serve as reliable containers for chemicals, reagents, and scientific materials in laboratories. In the construction sector, these tanks find utility in both temporary and permanent storage solutions for water, fuels, and construction materials, thanks to their durability and resilience against external elements.
Stainless steel tanks find various uses in residential settings, such as for storing domestic water, harvesting rainwater, and supporting irrigation systems. Thanks to its corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel is a top choice for these applications, ensuring a clean and safe water supply.
In essence, stainless steel tanks find extensive use across multiple sectors, including food and beverage, water, gas, pharmaceuticals, wastewater treatment, chemicals, hazardous materials, industry, education, construction, and residential settings. Their resistance to corrosion, exceptional durability, and hygienic qualities make them a dependable solution for storing, processing, and transporting a variety of substances in numerous industries.
Stainless Steel Tank Considerations
When acquiring storage solutions from a stainless steel tank manufacturer or supplier, several standard customer considerations come into play. Given that storage tanks can differ significantly and are frequently used for hazardous materials, it’s crucial to ensure that the supplier can offer both custom and high-quality solutions. Evaluate the depth of expertise and capabilities of the supplier’s engineering team, fabrication facilities, and field crew distribution, among other factors.
To assess a supplier’s value, we often evaluate their accreditation level and adherence to industry-specific standards. Professional standards and environmental regulations can vary depending on what a steel tank is designed to hold. For instance, in the oil and energy sector, using established standards is crucial for selecting a reliable supplier. The American Petroleum Institute (API) and the Petroleum Equipment Institute (PEI) emerged in the twentieth century, alongside the rapid growth of the petroleum industry. Today, they are highly regarded for their standards on storage tanks and guidelines for their use and maintenance. For instance, the API 650 specification is a prominent standard for regulating oil storage in steel tanks. Opting for a manufacturer who is an API member ensures adherence to the latest safety standards and industry practices.
When selecting the right storage tanks for your business, it’s crucial to consider the tank’s intended application, as this influences the key factors to look for. For instance, if the tank will primarily be used for mixing, its geometry becomes vital to achieve well-balanced mixes efficiently. Conversely, for storing water in residential buildings, offices, or similar settings, durability and material construction of steel tanks are more significant than their physical shape. Opting for a supplier with extensive experience will provide expert guidance to help you choose the most suitable tank for your commercial needs.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for You
No matter how much information you gather, you won’t get a superior stainless steel tank, and possibly not even a good one, unless you work with the right manufacturer. Who is the right manufacturer? It’s the one who understands your requirements, has the capability to meet them, can work within your budget and timeline, and can deliver as promised. Furthermore, the ideal manufacturer will offer exceptional customer service. To find such a company, explore the stainless steel tank manufacturers listed on this page. Dive in and begin your search. Best of luck!






 55 Gallon Drums
55 Gallon Drums Floor Gratings
Floor Gratings Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Plastic Containers
Plastic Containers Plastic Pallets
Plastic Pallets Plastic Tanks
Plastic Tanks Steel Shelving
Steel Shelving Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless Steel Tanks Storage Racks
Storage Racks Work Benches
Work Benches Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services